Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a hallmark of world-class manufacturing operations, enabling companies to identify, analyze, and mitigate the underlying causes of production issues.
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) stands out for its structured approach to dissecting complex system failures among the various RCA methods. By identifying potential combinations of failures leading to a top event, FTA helps manufacturers enhance their system reliability, safety, and efficiency.
Overview of Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) is a top-down, deductive failure analysis technique that systematically breaks down system failures into their constituent parts. It uses Boolean logic to combine a series of lower-level events,
This method is particularly relevant in the manufacturing industry, where it helps identify potential failure points and improve overall system robustness.
What is Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)?
FTA is a systematic method for identifying the root causes of potential system failures. It starts with a top event (the system failure) and works downward, breaking it into intermediate and basic events. This deductive approach allows manufacturers to understand how different factors interact to cause system failures.
History and Background
FTA was developed in the 1960s by Bell Laboratories for the U.S. Air Force to improve the safety of missile systems. Its effectiveness in identifying potential failure points led to its adoption across various high-stakes industries, including aerospace, nuclear power, and manufacturing. Today, FTA is a standard tool in safety and reliability engineering, known for its comprehensive and systematic approach to failure analysis.
The Structure of a Fault Tree
- Top Event: The primary system failure is being analyzed. It is the starting point of the fault tree.
- Intermediate Events: These events occur between the top event and the basic events, acting as links that connect the root causes to the top failure.
- Basic Events: The fundamental root causes or failures that contribute to the intermediate and top events. These are the lowest-level events in the fault tree.
Symbols and Notations
FTA uses specific symbols to represent different types of events and logic gates:
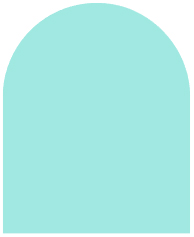
AND Gate
Represents a situation where multiple events must occur simultaneously to cause the next event. It is depicted as a flat-topped triangle.
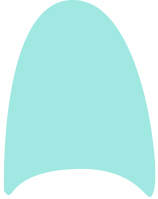
OR Gate
Represents a situation where any one of several events can cause the next event. It is depicted as a curved-topped triangle.
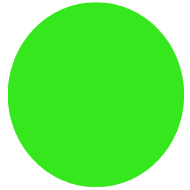
Basic Event Symbol
Typically shown as a circle, this represents a basic, root-level event.
Example Diagram:
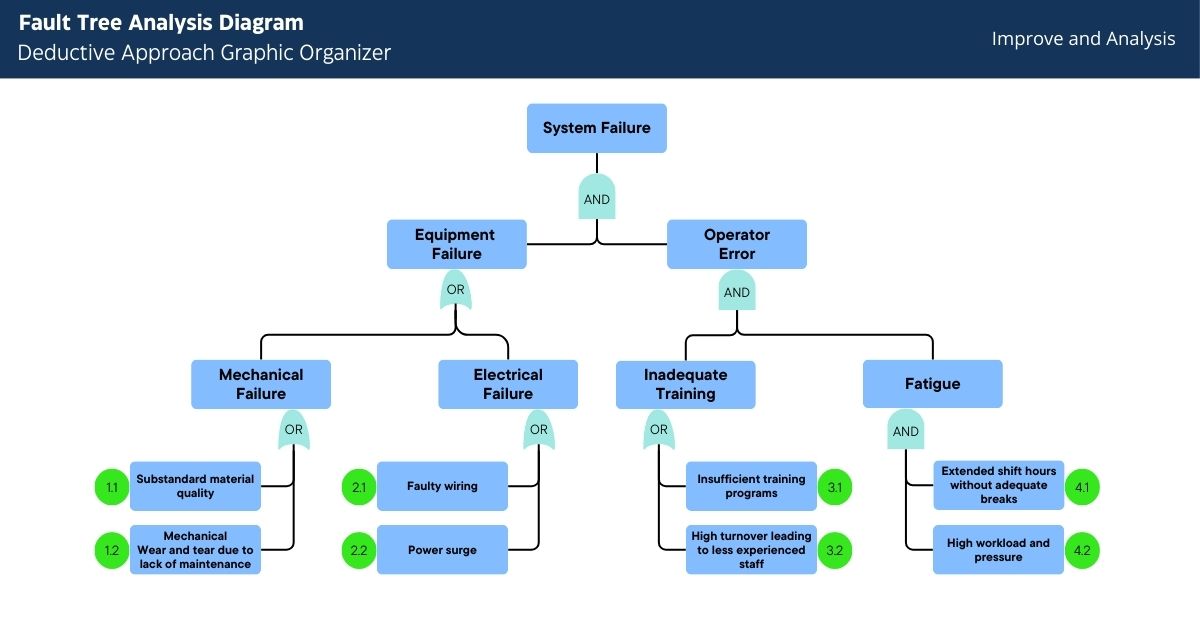
- Top Event: System Failure
- AND Gate: Requires both Power Failure and Component Failure to cause System Failure.
- AND Gate – Equipment Malfucntions
- Mechanical Failure:
- Root Cause 1.2: Wear and tear due to lack of maintenance: This might involve inadequate maintenance schedules or practices that do not align with the equipment’s usage demands.
- Root Cause 1.2: Substandard material quality: Using low-quality materials in the manufacturing of components can lead to quicker degradation and failures.
- Electrical Failure:
- Root Cause 2.1: Faulty wiring: Poor installation practices or subpar wiring materials can lead to electrical failures.
- Root Cause 2.2: Power surge: External factors like lightning strikes or internal issues such as unstable power supply can cause power surges.
- Mechanical Failure:
- OR Gate – Operator Error
- Inadequate Training:
- Root Cause 3.1: Insufficient training programs: When training programs are not comprehensive or updated, operators may lack critical knowledge.
- Root Cause 3.2: High turnover leading to less experienced staff: Frequent staff changes can result in a workforce with less cumulative experience.
- Fatigue:
- Root Cause 4.1: Extended shift hours without adequate breaks: Long working hours without proper rest can lead to operator fatigue and errors.
- Root Cause 4.2: High workload and pressure: Excessive workloads and high-pressure environments can contribute to mental and physical fatigue.
- Inadequate Training:
The Process of Conducting an FTA
- Define the Top Event: Clearly identify and describe the primary failure to be analyzed. This could be a system shutdown, a safety incident, or any significant operational failure.
- Construct the Fault Tree: Develop the fault tree by breaking down the top event into intermediate and basic events using Boolean logic. This involves identifying all possible contributing factors and how they interrelate.
- Analyze the Fault Tree: Evaluate the likelihood of different combinations of events leading to the top event. This analysis helps prioritize which root causes need immediate attention.
- Identify and Implement Solutions: Develop and implement strategies to mitigate or eliminate the root causes identified. This could involve redesigning processes, improving maintenance practices, or enhancing training programs.
In a manufacturing plant, the top event might be a production line stoppage. The fault tree would break this down into intermediate events, such as equipment failure and operator error, which are further broken down into basic events, like maintenance neglect and inadequate training.
Benefits of FTA in Manufacturing
Enhanced Problem-Solving
FTA provides a structured and logical approach to problem-solving. By systematically breaking down failures into their root causes, it ensures that all potential contributing factors are considered, leading to more effective and comprehensive solutions.
Improved Safety and Reliability
In the manufacturing industry, safety and reliability are paramount. FTA helps identify and address potential failures before they occur, enhancing the overall safety and reliability of manufacturing processes. This proactive approach can prevent accidents and improve operational efficiency.
Cost Savings
Preventing failures through FTA can lead to significant cost savings. By identifying and addressing potential issues early, manufacturers can avoid costly downtime, reduce waste, and minimize the need for expensive repairs. This not only improves the bottom line but also enhances product quality and customer satisfaction.
Practical Applications of FTA in Manufacturing
- Automotive Industry: An automotive manufacturer used FTA to address recurring assembly line stoppages. By identifying the root causes, such as equipment malfunctions and operator errors, the company implemented preventive measures that significantly reduced downtime and improved productivity.
- Electronics Manufacturing: An electronics company applied FTA to analyze failures in its production process. By identifying root causes like component defects and process inconsistencies, the company improved product quality and customer satisfaction, leading to increased market competitiveness.
Industry Examples
FTA is particularly useful in sectors where system reliability and safety are critical. In the automotive industry, FTA can help prevent vehicle recalls by identifying potential failures during the manufacturing process. In electronics manufacturing, it can improve the reliability of products, reducing returns and warranty claims.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing FTA can be complex and resource-intensive. It requires detailed knowledge of the system being analyzed and can be time-consuming. Additionally, constructing an accurate and comprehensive fault tree requires expertise and collaboration across different departments.
Best Practices
- Thorough Documentation: Maintain comprehensive records of all steps and findings. This ensures transparency and facilitates future reviews.
- Team Collaboration: Involve cross-functional teams to ensure all potential failure modes are considered. This collaborative approach can provide diverse perspectives and enhance the accuracy of the fault tree.
- Regular Reviews: Periodically review and update the fault tree to reflect changes in the system or process. This ensures that the fault tree remains relevant and accurate over time.
Conclusion for Manufacturing Leadership
FTA is a powerful tool for identifying and addressing potential failures in manufacturing processes. Its systematic approach enhances problem-solving, safety, reliability, and cost savings. By breaking down complex system failures into their root causes, FTA helps manufacturers improve their operations and prevent future issues.
Manufacturers should consider adopting FTA as part of their root cause analysis toolkit.
Through proactive identification and resolution of potential failures, companies can optimize their operational efficiency, enhance product quality, and guarantee the safety of their processes.
How POWERS Can Help with Root Cause Analysis
POWERS specializes in enhancing manufacturing productivity through tailored, results-based management consulting. Our unique approach drives higher productivity and efficiency. With substantial experience in operations, finance, and human resources, our team works directly with your leadership to implement effective root cause analysis techniques like FTA. This hands-on method ensures sustainable improvements and measurable ROI.
Contact us today for expert assistance in root cause analysis to elevate your manufacturing processes and achieve lasting success.
- Speak to an Expert: Call +1 678-971-4711 to discuss your specific challenges and goals.
- Email Us: Get tailored insights by emailing info@thepowerscompany.com
- Request an Assessment: Use our online contact form, and one of our productivity experts will reach out to schedule an in-depth analysis of your operations.
Continue Reading from this Mastery Series
- Part 1 – The 5 Whys Technique Deep Dive
- Part 2 – Utilizing the Fishbone Diagram Deep Dive
- Part 3 – Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) in the Manufacturing Industry
- Part 4 – Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) Deep Dive
- Part 5 – Using Pareto Analysis to Uncover Productivity Killers







